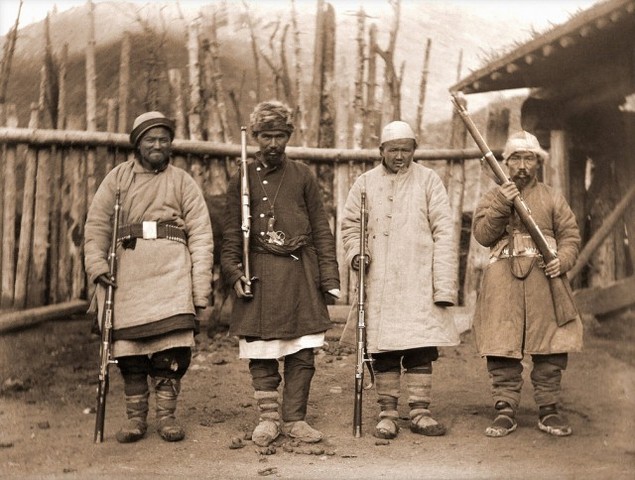
The history of the Xinhai Revolution began with the Wuchang Uprising, an armed rebellion against the Qing Dynasty rulers that broke out on October 10, 1911, in today's Wuchang District, Wuhan City, central China's Hubei Province. After Wuchang was taken, the revolutionaries quickly seized strategic locations Hanyang and Hankou, altogether known. 4 A survey of key work published in China on the 1911 revolution in the decade 2000-09 is Kaiyuan, Zhang and Tong, Tian, " Xin shiji zhi chu de Xinhai geming shi yanjiu " ("Research on the Xinhai revolution at the start of the new century"), Zhejiang shehui kexue, No. 9 (2010), pp. 89 - 98 Google Scholar. The aftermath of the. 
Chinese Revolution of 1911 by Abby Kiros
1,000 year old social system. 4,000 year old monarchy. Causes of the Revolution of 1911. 1) Elite politics with widespread support, against: 250 year old Qing Dynasty. 1,000 year old social system. 4,000 year old monarchy. 2) Corrupt and inefficient government. 3) Foreign intervention. The first revolution, in 1911, aimed to rid the country of the Manchus and to set up a republic modeled on the governments of the United States and Great Britain. It was comparatively simple to overthrow the Manchu Dynasty. It fell because it was too rotten to stand.
The revolution was named Xinhai (Hsin-hai) because it occurred in 1911, the year of the Xinhai stem-branch in the sexagenary cycle of the Chinese calendar. The revolution consisted of many revolts and uprisings. The turning point was the Wuchang uprising on 10 October 1911, which was the result of the mishandling of the Railway Protection Movement. Before the 1997 CPC National Congress, it was believed that the greatest historic achievement of the 1911 Revolution was that it overthrew the decadent Qing Dynasty (1644-1911), ended the 2,000-year-old autocratic monarchy and established the first bourgeois republic in China.
Chinese Revolution 1911 1949 timeline Timetoast timelines
Launched by Chinese revolutionaries represented by Sun Yat-sen, the 1911 Revolution began with the Wuchang Uprising, an armed rebellion against the Qing Dynasty rulers that broke out on October 10, 1911 in what is today's Wuchang District, Wuhan City, in central China's Hubei Province. The revolt overthrew the six-year-old Emperor Puyi, and in 1912 opposition leaders established a Chinese republic. Lithograph illustrating the 1911 battle at Ta-ping gate, Nanking. From the Wellcome Library, London, CC BY 2.0. Nationalists vs. communists (except during WWII)
The revolution started 110 years ago and saw the end of the Qing dynasty and the birth of a new China The long term consequences of the Chinese Revolution is the end of a four thousand year monarchy to turn China to develop under the idea of socialism, switching people's belief of not accepting manchuism to imperialism, an increase of modernizing people lives in culture from western ideas and the establishment of the Republic of China, which all. 
PPT Chapter 22 Section 2 Revolution in China PowerPoint
The Wuchang Uprising was an armed rebellion against the ruling Qing dynasty that took place in Wuchang (now Wuchang District of Wuhan), Hubei, China on 10 October 1911, beginning the Xinhai Revolution that successfully overthrew China's last imperial dynasty. It was led by elements of the New Army, influenced by revolutionary ideas from Tongmenghui. The uprising and the eventual revolution. Another defeat for the Qing results in a treaty forcing the legalisation of opium and Christianity. This humiliating defeat gives rise to the Self Strengthening Movement, an attempt to industrialise China and increase her capacity for self-defence.. "Chinese Revolution timeline: to 1911, Alpha History, accessed [today's date], https.
The flash-point came on 10 October 1911, with the Wuchang Uprising, an armed rebellion among members of the New Army. Similar revolts then broke out spontaneously around the country, and revolutionaries in all provinces of the country renounced the Qing dynasty. The Chinese Revolution (1911-12) Li Yuanhong The Chinese Revolution was triggered not by the United League itself but by the army troops in Hubei who were urged on by the local revolutionary bodies not incorporated in the league. 
La r volution de 1911 cons cration de Sun Yat sen Chine Magazine
In 1910, the Chinese Empire reasserted itself and occupied Tibet. However, this would be the decadent Empire's last triumph. All across China, revolutionary groups had formed to overthrow the regime, with one such group managing to seize power in the city of Wuchang on October 10, 1911. From there the revolution spread quickly, and, in January 1912, China was declared a republic. Chinese Revolution, (1911-12), nationalist democratic revolt that overthrew the Qing (or Manchu) dynasty in 1912 and created a republic. Ever since their conquest of China in the 17th century, most of the Manchu had lived in comparative idleness, supposedly a standing army of occupation but in reality inefficient pensionaries.